Chapter 2 Communication
2.1 Networking
Networking devices
LAN - local area network
A typical LAN consists of a number of computers and devices (such as printers) connected to hubs or switches. One of the hubs or switches is usually connected to a router and/or modem to allow the LAN to connect to the internet or become part of a WAN
WLAN - wireless LAN
Devices connected are known as wireless access points (WAPs)
WAN - wide area network - formed by a number of LANs connected together; large geo area
MAN - Metropolitan area network
Client-server and peer-to-peer networking models
client-server model - network that uses separate dedicated servers and specific client workstations. All client computers are connected to the dedicated servers
thin clients - heavily dependent on having access to a server
- pros: less expensive to expand, server can offer protection against hacking and malware
- cons: high reliance on server, start-up costs can be high
thick clients - can work offline or online
- pros: more robust (can work offline), clients have more control
- cons: less secure, data integrity
peer-to-peer model - network in which each node can share its files with all the other nodes. Each node has its own data and there is no central server
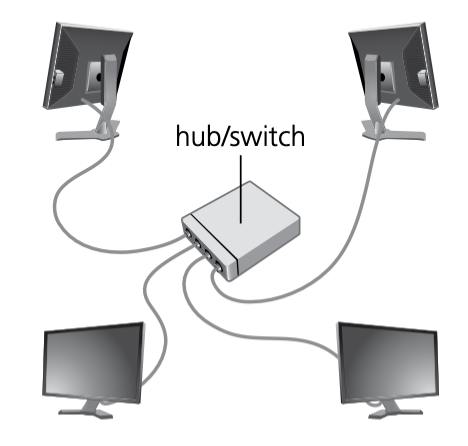
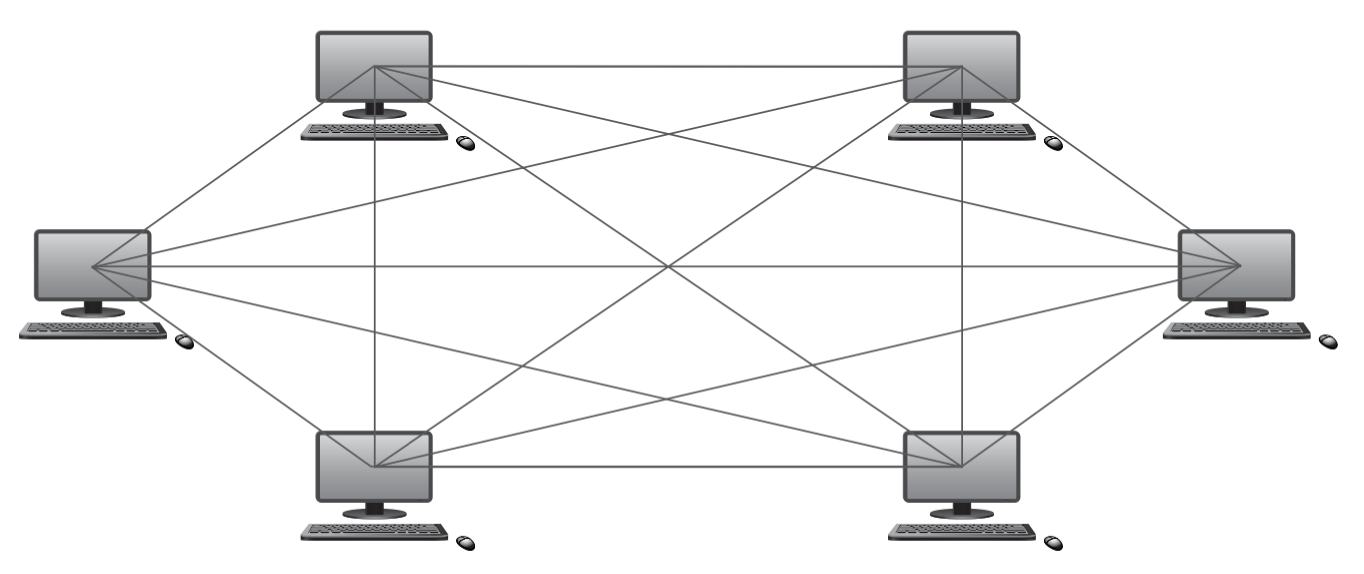
Network topologies
- bus networks

- star networks
- mesh networks
- hybrid networks
Public and private cloud computing
Cloud storage
- public cloud; private cloud; hybird cloud
- pros: access anywhere; a remote back-up to data; unlimited capacity
- cons: high cost; slow internet connection; potential failure of cloud storage company
Cloud software
Wired and wireless networking
Wireless
- Bandwidth: infrared > microwaves > radio waves
- Penetration: radio waves > microwaves > infrared
- Attenuation: radio waves > microwaves > infrared
WIred
- twisted pair cables
- coaxial cables
- fibre optic cables
Bit Streaming
contiguous sequence of bits, representing a stream of data, transmitted continuously over a communications path, serially (one at a time)
real-time streaming
- An event is captured live
- The video signal is encoded to streaming media files
- The encoded feed is then uploaded to a file server
- Streaming servers duplicate the feed and send it to all clients requesting it in real time
on-demand streaming - Video is stored on a server as streaming media files
2.2 The internet
Difference between Internet and WWW
Internet (interconnected network) - a massive network of networks, uses TCP/IP protocals
World Wide Web (WWW) - a collection of multimedia web pages and other documents which are stored on websites
Hardware and software needed to support the internet
- Public switched telephone network (PSTN)
- Phone calls using the internet
- Cellular networks and satellites
IP addresses
IPv4 - based on 32bits split into four groups of 8bits, each giving a range of 0 to 255
e.g. 192.25.0.255
network ID: 192.25.0
host ID: 255
IPv6 - based on 128-bit split into 8 groups of 16 bits, adopts the hexadecimal notation
e.g. A8FB:7A88:FFF0:0FFF:3D21:2085:66FB:F0FA
zero compression of IPV6
e.g. 900B:3E4A:AE41::AFF7:DD44:F1FF
Uniform resource locators (URL)
protocol://website address/path/filename
https://www.apple.com.cn/mac/index.html
website address: domain host (www) + domain name (apple) + domain type (.com) + (sometimes) a country code (.cn)
Sequence of Events when Viewing a Website
- User specifies a URL in their client
- Client sends DNS lookup request to convert URL to an IP address and initiates a TCP connection to server
- Server acknowledges TCP connection, client sends HTTP requests to retrieve content for the URL.
- Server replies with content for web page and browser retrieves content from the HTTP packets and renders
- Client-side script: code that runs on client written using language supported by browser e.g. Javascript. Enables web pages to be scripted; to have different and changing content depending on user input, or other variables.
- Server-side script: code that runs on server written using language supported by server e.g. PHP. Used to provide interface for client & to limit client access to databases